Unsupervised Multi-channel Speech Dereverberation via Diffusion
2025/02 - 2025/06, accepted by WASPAA 2025
We consider the problem of multi-channel single-speaker blind dereverberation, where multi-channel mixtures are used to recover the clean anechoic speech. To solve this problem, we propose USD-DPS, Unsupervised Speech Dereverberation via Diffusion Posterior Sampling. USD-DPS uses an unconditional clean speech diffusion model as a strong prior to solve the problem by posterior sampling. At each diffusion sampling step, we estimate all microphone channels’ room impulse responses (RIRs), which are further used to enforce a multi-channel mixture consistency constraint for diffusion guidance. For multi-channel RIR estimation, we estimate reference-channel RIR by optimizing RIR parameters of a sub-band RIR signal model, with the Adam optimizer. We estimate non-reference channels’ RIRs analytically using forward convolutive prediction (FCP). We found that this combination provides a good balance between sampling efficiency and RIR prior modeling, which shows superior performance among unsupervised dereverberation approaches. An audio demo page is provided in this URL.
Introduction
Why and what is dereverberation
- In real rooms, microphone arrays capture multi-channel reverberant mixtures which degrade performance in automatic speech recognition and hearing aids \(y=\left\{y_c \mid y_c=h_c * x_1+n_c, 1 \leq c \leq C\right\}\)
- Dereverberation aims to invert this process and recover the clean anechoic speech from mixtures.
Strengths of our USD-DPS method
- Unsupervised: no paired clean/reverb data needed
- Powerful priori: Leverages a pre-trained clean-speech diffusion model
- Hybrid RIR estimation: efficient analytic FCP for non-ref channels + optimized ref-channel RIR, leveraging multi-channel information with a small demand of computing
Backgrounds
Score-Based Diffusion
Score-based models learn $\nabla_x \log p(x)$ via a DNN, and sample by solving the probabilistic flow ODE: \(d x_1^\tau = -\,\sigma(\tau)\,\nabla_{x_1^\tau}\log p\!\left(x_1^\tau\right)\, d\tau\)
Diffusion Posterior Sampling (DPS)
DPS solves inverse problems by sampling from the posterior $p!\left(x_1 \mid y\right)$ using: \(d x_1^\tau = -\,\sigma(\tau)\,\nabla_{x_1^\tau}\log p\!\left(x_1^\tau \mid y\right)\, d\tau\)
With Bayes’ rule and Tweedie’s formula, the posterior score can be decomposed/approximated as: \(\nabla_{x_1^\tau}\log p\!\left(y \mid x_1^\tau\right) = \nabla_{x_1^\tau}\log p\!\left(y \mid x_1^\tau, h\right) \simeq \nabla_{x_1^\tau}\log p\!\left(y \mid \hat{x}_1^0, h\right)\)
BUDDy and RIR Model
Each frequency band undergoes independent 1D convolution: \(Y_{m,k}=H_{m,k} * X_{m,k}=\sum_{n=0}^{N_h-1} H_{n,k}\, X_{m-n,k}\)
RIR is parameterized as $\psi=\bigl{\Phi,\,(w_b,\alpha_b)_{b=1}^B\bigr}$
- Magnitude response $A \in \mathbb{R}^{N_h \times K}: \quad A’_{n,b}=w_b\,e^{-\alpha_b n}, A=\exp!\bigl(\operatorname{lerp}(\log A’)\bigr)$
- Phase $\Phi \in \mathbb{R}^{N_h \times K}$
RIR model is optimized by: \(\hat{\psi} =\underset{\psi}{\operatorname{argmin}} \;\Bigl\| S_{\mathrm{comp}}(y_1)-S_{\mathrm{comp}}\!\bigl(\mathcal{A}_\psi(\hat{x}_1^0)\bigr) \Bigr\|_2^2 + R(\psi)\)
Forward Convolutive Prediction (FCP)
For each non-reference channel, estimate a forward convolutive filter: \(\begin{aligned} \hat{H}^c &=\mathrm{FCP}\!\left(Y^c,\hat{X}\right) =\underset{H^c}{\operatorname{argmin}} \sum_{m,k} \frac{1}{\hat{\lambda}_{m,k}^c} \left| Y_{m,k}^c-\sum_{n=0}^{N_h'-1} H_{n,k}^c\,\hat{X}_{m-n,k} \right|^2 \\ \hat{\lambda}_{m,k}^c &=\frac{1}{C}\sum_{c=1}^C \left|Y_{m,k}^c\right|^2 +\epsilon \cdot \max_{m,k}\left[ \frac{1}{C}\sum_{c=1}^C \left|Y_{m,k}^c\right|^2 \right] \end{aligned}\)
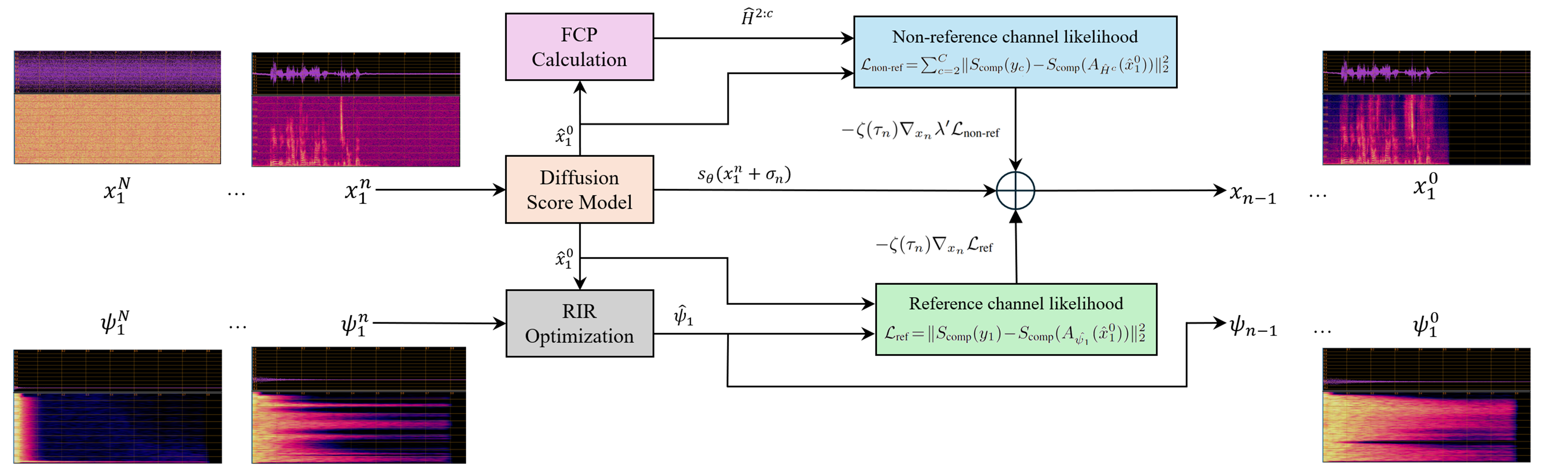
Proposed Method: USD-DPS
We adopt a hybrid likelihood score estimation for reference and non-reference channels. At each diffusion step, we guide the diffusion model by optimizing RIR/FCP models.
Reference Channel: RIR Model
During each diffusion step, a parametric RIR model $\hat{\psi}_1$ for the reference channel is optimized by Adam. The reconstruction loss is: \(\mathcal{L}_{\text{ref}} =\left\| S_{\text{comp}}(y_1) - S_{\text{comp}}\!\bigl(A_{\hat{\psi}_1}(\hat{x}_1^0)\bigr)\right\|_2^2\)
Non-reference Channels: FCP Models
We estimate FCP models $\widehat{H}^{2:c}$ for each pair of estimated clean speech and non-reference channel. The non-reference reconstruction loss is: \(\mathcal{L}_{\text{non-ref}}=\sum_{c=2}^{C}\left\|S_{\text{comp}}(y_c)-S_{\text{comp}}\!\bigl(A_{\hat{H}^c}(\hat{x}_1^0)\bigr)\right\|_2^2\)
Likelihood Score Calculation
We combine the two losses with a tunable coefficient $\lambda’$ and take the derivative w.r.t. $x_1^\tau$ to obtain the likelihood score: \(\nabla_{x_1^\tau}\log p\!\left(y \mid x_1^\tau\right)\simeq\zeta(\tau)\,\nabla_{x_1^\tau}\!\Biggl(\left\|S_{\text{comp}}(y_1)-S_{\text{comp}}\!\bigl(A_{\hat{\psi}_1}(\hat{x}_1^0)\bigr)\right\|_2^2 + \lambda'\sum_{c=2}^{C}\left\|S_{\text{comp}}(y_c)-S_{\text{comp}}\!\bigl(A_{\hat{H}^c}(\hat{x}_1^0)\bigr)\right\|_2^2\Biggr)\)
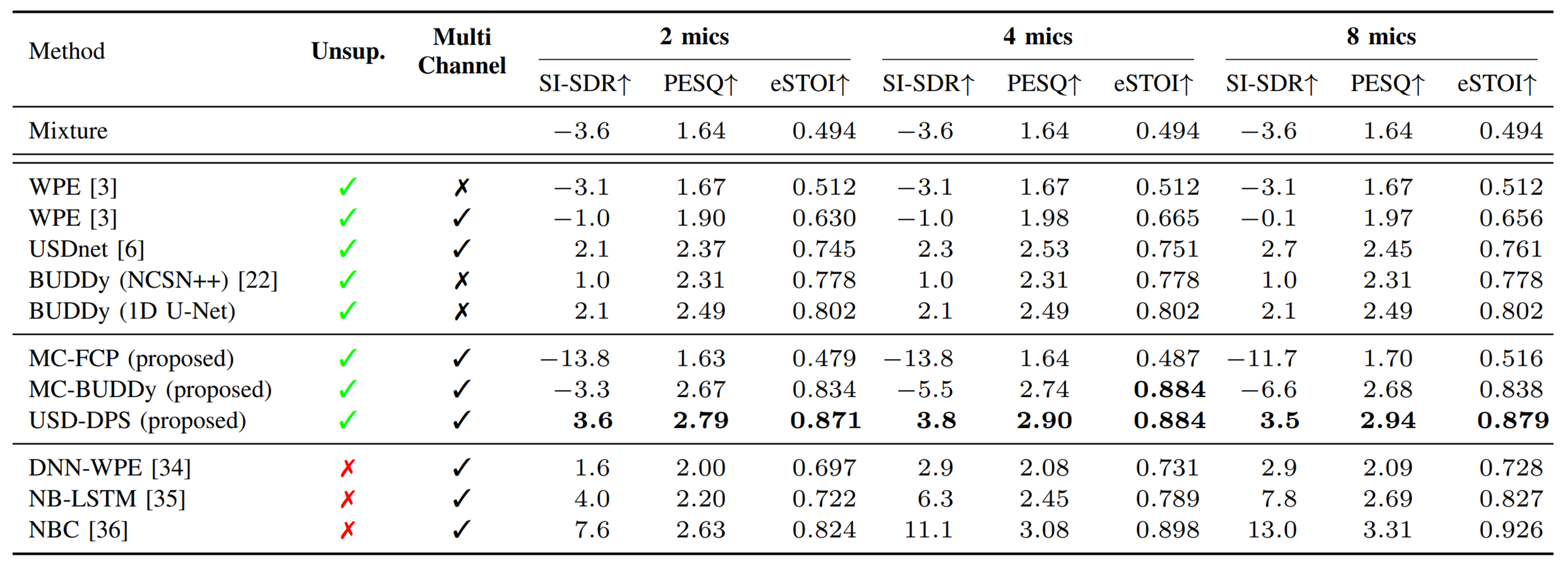
Experiment Results (SI-SDR, PESQ, ESTOI)