Electronic Music Synthesis Notes
UIUC MUS 102 Notes
Images can be made zoomable. Simply add data-zoomable to <img> tags that you want to make zoomable.
Course Overview
This course surveys computer music and audio digital signal processing (DSP) with an emphasis on spectral analysis/synthesis, psychoacoustics, physical and modal modeling, room acoustics, and modern modulation and cross-synthesis techniques. You will learn how sound is analyzed, represented, transformed, and resynthesized for music technology, alongside practical insights into human hearing and real-world audio systems.
Learning Outcomes
By the end, students should be able to:
- Explain core psychoacoustic concepts (critical bands/Bark scale, masking, place principle) and apply them to analysis and synthesis.
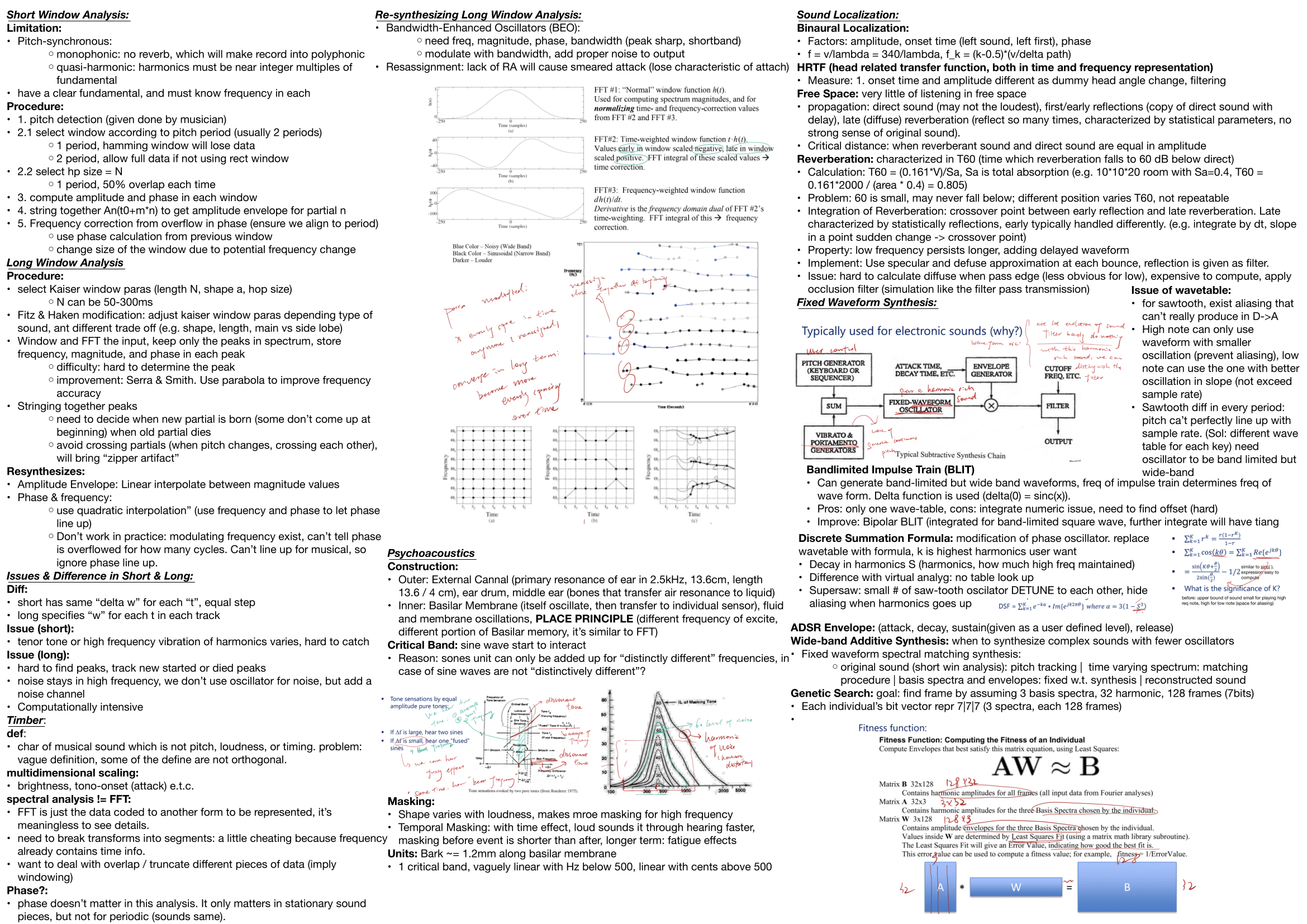
- Perform short-window (pitch-synchronous) and long-window spectral analysis, peak picking, and track partials; understand reassignment for sharpened time-frequency localization.
- Implement and compare additive, wavetable, BLIT/DSF, granular, AM/FM/SSB methods; reason about aliasing and bandlimiting.
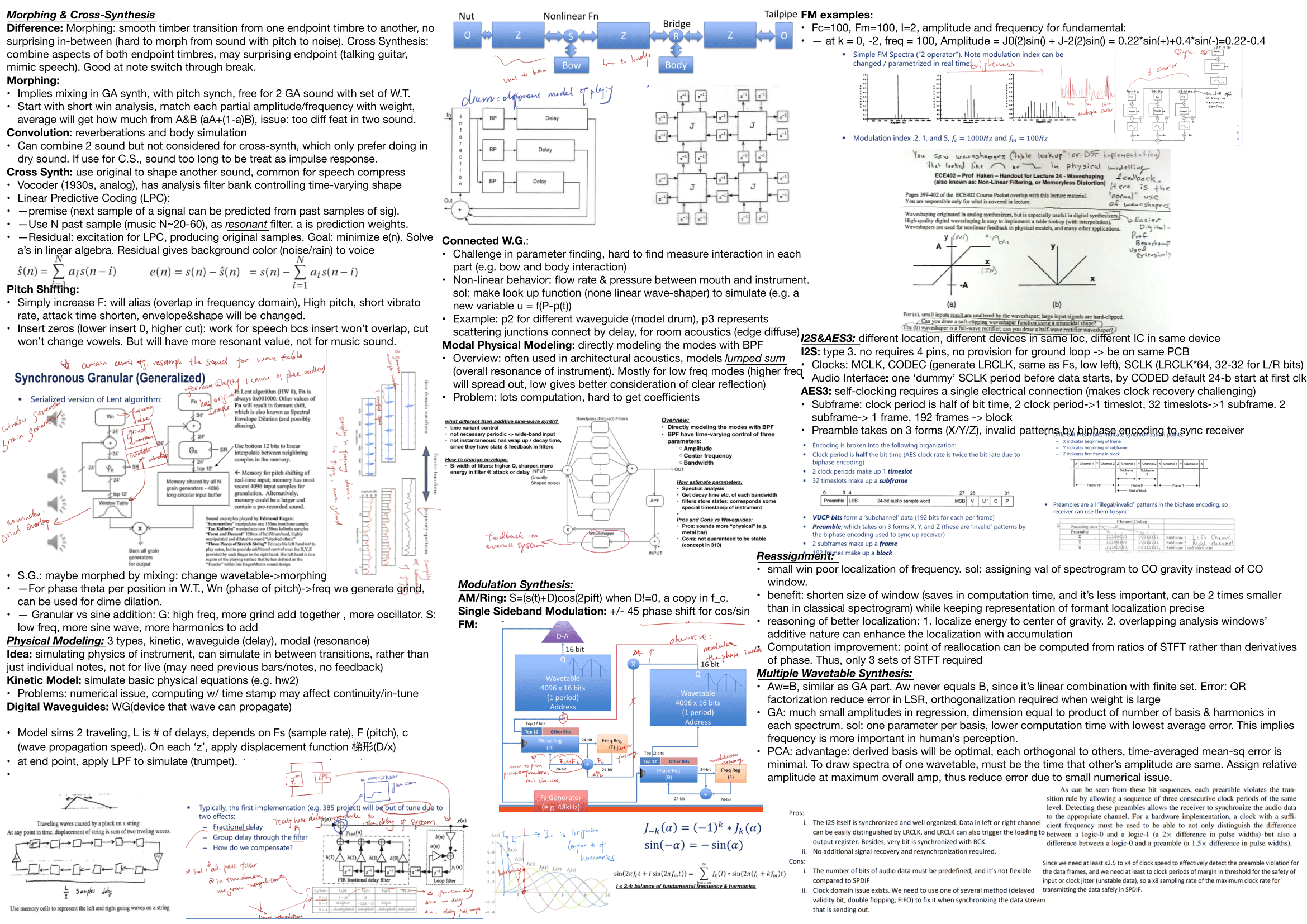
- Apply cross-synthesis approaches (vocoder, LPC) and morphing between timbres.
- Model instruments and acoustics via digital waveguides, modal and kinetic models; reason about nonlinearity and parameterization.
- Analyze room acoustics (direct/early/late energy, critical distance, T60) and practical reverberation/convolution workflows.
- Understand audio I/O interfaces (I2S, AES3) and clocking at a block/bit level.
Syllabus (Modules)
Organized by topic clusters so you can map to weeks as needed.
1) Psychoacoustics & Timbre
- Ear anatomy & place principle on the basilar membrane
- Critical bands / Bark scale; loudness and masking (spectral & temporal)
- What defines timbre (brightness, attack, etc.); multidimensional scaling notions
2) Time–Frequency Analysis
- Short-window, pitch-synchronous analysis: assumptions (monophonic, quasi-harmonic), window length vs. overlap, amplitude/phase tracking, phase-overflow correction
- Long-window (Kaiser/Fitz-Haken tuning): peak detection, parabolic interpolation (Serra & Smith), partial birth/death & “zipper” artifacts
- Reassignment spectrograms: center-of-gravity relocation to sharpen attacks and formants; computational shortcuts via STFT ratios
3) Additive & Wavetable Synthesis
- Additive resynthesis from tracked partials; envelopes for magnitude/phase
- Fixed-waveform spectral matching (basis spectra + time-varying envelopes)
- Multiple wavetables: least-squares/QR, orthogonalization; PCA for optimal bases; genetic search heuristics
- Supersaw detuning to mask aliasing / enrich spectra
4) Bandlimited Oscillation & Aliasing Control
- BLIT (bandlimited impulse train) and bipolar BLIT; numerical integration caveats
- DSF (Discrete Summation Formula): harmonic roll-off control (S parameter)
- Practical aliasing constraints vs. sampling rate, table size, and key-mapped tables
5) Modulation & Pitch Processing
- AM / Ring modulation (carrier/offset images), SSB via ±90° phasing
- FM spectral structure (Bessel-function sidebands, index control)
- Pitch shifting trade-offs (aliasing, envelope/attack changes); speech-specific zero-insertion vs. musical content
6) Cross-Synthesis & LPC
- Vocoder analysis banks driving timbre shaping
- LPC: linear prediction, residual/excitation, filter interpretation; speech-music cross-applications
- Morphing vs. cross-synthesis (contrast; when each is appropriate)
7) Physical & Modal Modeling
- Digital waveguides (traveling waves, delays, boundary filters), junction scattering, room/edge diffusion ideas
- Modal modeling (low-frequency modes; architectural acoustics focus), parameter estimation challenges
- Kinetic (finite-difference) approaches and stability/continuity considerations
- Handling nonlinearities (reed/bow mouthpiece lookup, waveshaping)
8) Room Acoustics & Reverberation
- Direct, early reflections, late diffuse field; critical distance
- T60 estimation & Sabine-type calculations; issues with position dependence and dynamic-range limits
- Energy decay integration and crossover points; low-frequency persistence
- Convolution for reverberation and body responses; occlusion/edge-diffusion approximations
9) Practical Spectral Resynthesis
- Envelope interpolation; phase/frequency handling under modulation
- Noise channels for high-frequency residuals; when/why phase alignment is unnecessary in musical reconstructions
- Computational concerns and artifact mitigation
10) Audio Interfaces & Clocking
- I2S (MCLK/LRCLK/SCLK roles; word framing), same-board constraints
- AES3 framing (subframes/frames/blocks), preambles (X/Y/Z), biphase mark and clock recovery
Tools & Techniques You Should Be Comfortable With
- STFT/ISTFT with window/overlap choice; Kaiser/Hamming/Hann selection
- Peak picking & parabolic interpolation; partial tracking heuristics
- Using reassignment to improve TF localization
- Constructing bandlimited oscillators (BLIT/DSF) and diagnosing aliasing
- Building FM/AM/SSB blocks and reading their spectra
- Implementing simple LPC analysis–synthesis loops
- Designing waveguide building blocks and small modal banks
- Calculating T60/critical distance and doing simple room-IR convolution
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: